Materials from E-Poster presented at rstudio::conf(2020).
Das, D., Li, A., & Simeon, K. (2020, January). Teaching R Outside the Classroom: Supporting Instructors and Learners. E-Poster presented at rstudio::conf(2020), San Francisco, CA.
This repo contains the .pdf and a .png version of our poster and other relevant materials.
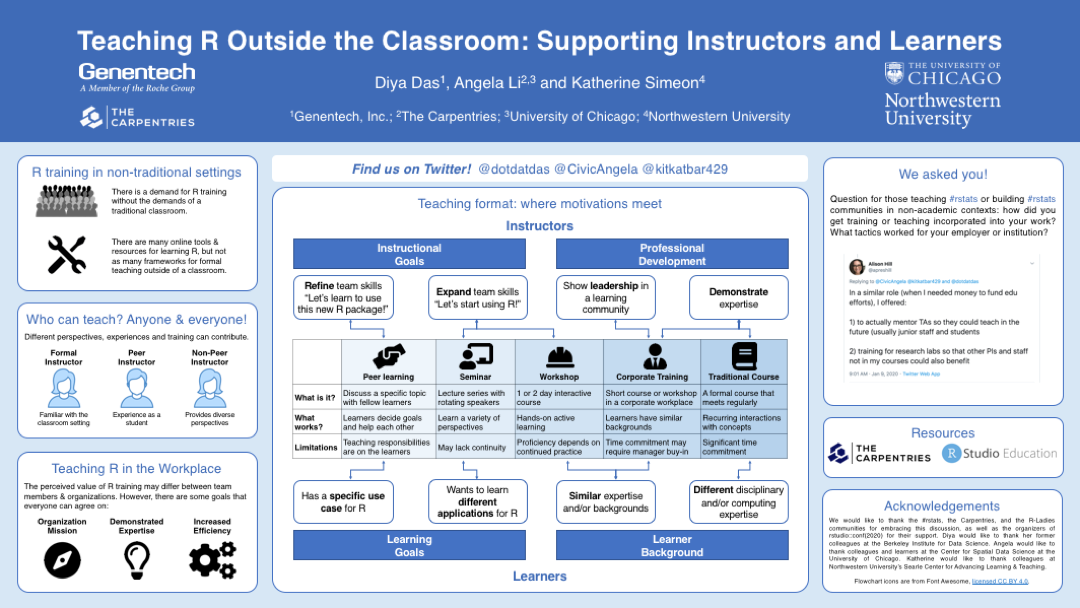
During the poster presentation, the poster contained a gif that rotated through a twitter discussion re: how we incorporate teaching into our work (top right). For readability, a link to this Twitter thread is included in the .pdf version in lieu of the gif. Additionally, you can see the images used the generate the poster gif in the rstats-tweets subdirectory.
There is considerable variability how individuals learn R. While many formal courses, both online and in-person, are available to learners, typical methods of learning are acquiring knowledge on-the-job and participating in short-term trainings such as single-session or multi-day workshops. While these non-traditional contexts are highly successful, instructors are challenged to capitalize on a limited amount of time and cater to an audience with learners of different backgrounds and levels of experience.
A non-traditional learning environment has the potential to implement the best practices of a traditional classroom (e.g., goal-setting through specific, achievable learning objectives) while taking advantage of active learning strategies that engage learners and establish a collaborative environment where learners can learn from each other as much as from the instructor (e.g., forming peer learning groups, providing more time for coding exercises).
However, there is a need for best practices and shared resources for disseminating and utilizing these strategies. Additionally, there is ample opportunity to tailor this specifically for R education. What are the standards for these informal courses for teaching applications of a programming language, and how can we evaluate the success of these opportunities for different audiences and objectives? What types of support could improve instructor experiences? How can the learner experience be improved, from adoption of instructional techniques to the integration of other resources? Can pedagogical techniques commonly employed in more formal contexts, such as active learning, be adapted to much shorter periods of instruction? How can advances in educational technology can support the teaching of R and RStudio in synchronized contexts? And finally, how do we ensure that learners are able to apply and extend what they’ve learned beyond this short-form educational opportunity and attendant resources?
Diya Das
Angela Li
Katherine Simeon
We've added a subdirectory with related resources here.