 |
hyperdrive: an algorithmic trading library |
|---|
hyperdrive is an algorithmic trading library that powers quant research firm ![]() FORCEPU.SH.
FORCEPU.SH.
Unlike other backtesting libraries, hyperdrive specializes in data collection and quantitative research.
In the examples below, we explore how to:
- store market data
- create trading strategies
- test strategies against historical data (backtesting)
- execute orders.
You will need Python 3.8+
To install the necessary packages, run
pythom -m pip install hyperdrive -U
Most secrets must be passed as environment variables. Future updates will allow secrets to be passed directly into class object (see example on order execution).
Pre-requisites:
- a Polygon API key
- an AWS account and an S3 bucket
Environment Variables:
POLYGONAWS_ACCESS_KEY_IDAWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEYAWS_DEFAULT_REGIONS3_BUCKET
from hyperdrive import DataSource
from DataSource import Polygon, MarketData
# Polygon API token loaded as an environment variable (os.environ['POLYGON'])
symbol = 'TSLA'
timeframe = '7d'
md = MarketData()
poly = Polygon()
poly.save_ohlc(symbol=symbol, timeframe=timeframe)
df = md.get_ohlc(symbol=symbol, timeframe=timeframe)
print(df)
Output:
Time Open High Low Close Vol
2863 2021-11-10 1010.41 1078.1000 987.31 1067.95 42802722
2864 2021-11-11 1102.77 1104.9700 1054.68 1063.51 22396568
2865 2021-11-12 1047.50 1054.5000 1019.20 1033.42 25573148
2866 2021-11-15 1017.63 1031.9800 978.60 1013.39 34775649
2867 2021-11-16 1003.31 1057.1999 1002.18 1054.73 26542359
Much of this code is still closed-source, but you can take a look at the Historian class in the History module for some ideas.
We use vectorbt to backtest strategies.
from hyperdrive import History, DataSource, Constants as C
from History import Historian
from DataSource import MarketData
hist = Historian()
md = MarketData()
symbol = 'TSLA'
timeframe = '1y'
df = md.get_ohlc(symbol=symbol, timeframe=timeframe)
holding = hist.from_holding(df[C.CLOSE])
signals = hist.get_optimal_signals(df[C.CLOSE])
my_strat = hist.from_signals(df[C.CLOSE], signals)
metrics = [
'Total Return [%]', 'Benchmark Return [%]',
'Max Drawdown [%]', 'Max Drawdown Duration',
'Total Trades', 'Win Rate [%]', 'Avg Winning Trade [%]',
'Avg Losing Trade [%]', 'Profit Factor',
'Expectancy', 'Sharpe Ratio', 'Calmar Ratio',
'Omega Ratio', 'Sortino Ratio'
]
holding_stats = holding.stats()[metrics]
my_strat_stats = my_strat.stats()[metrics]
print(f'Buy and Hold Strat\n{"-"*42}')
print(holding_stats)
print(f'My Strategy\n{"-"*42}')
print(my_strat_stats)
# holding.plot()
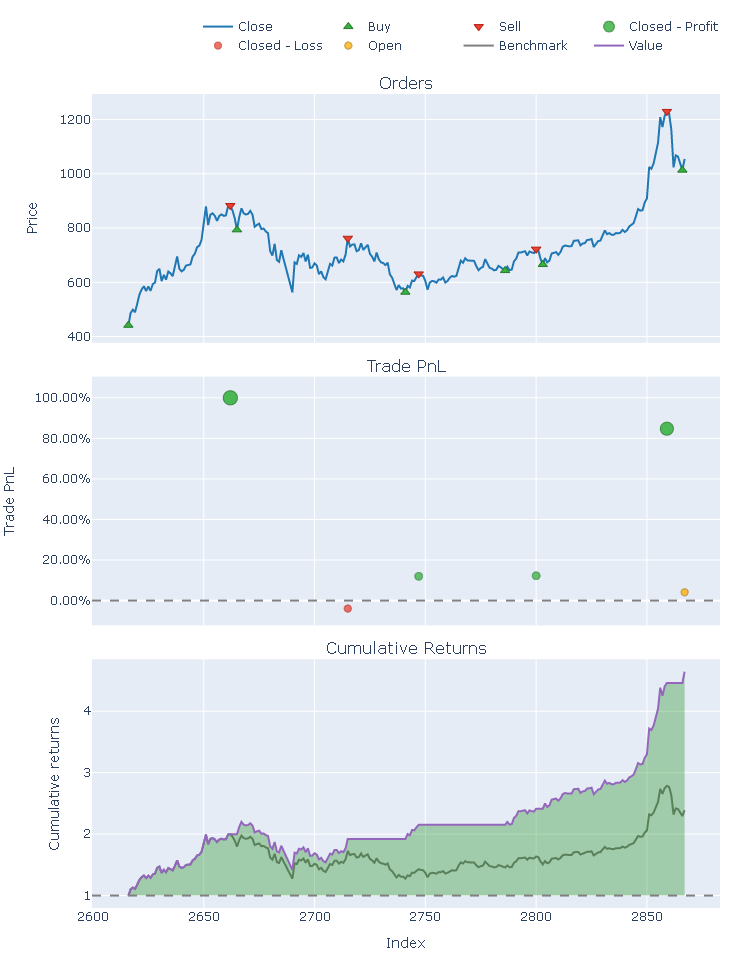
my_strat.plot()
Output:
Buy and Hold Strat
------------------------------------------
Total Return [%] 138.837436
Benchmark Return [%] 138.837436
Max Drawdown [%] 36.246589
Max Drawdown Duration 186 days 00:00:00
Total Trades 1
Win Rate [%] NaN
Avg Winning Trade [%] NaN
Avg Losing Trade [%] NaN
Profit Factor NaN
Expectancy NaN
Sharpe Ratio 2.206485
Calmar Ratio 6.977133
Omega Ratio 1.381816
Sortino Ratio 3.623509
Name: Close, dtype: object
My Strategy
------------------------------------------
Total Return [%] 364.275727
Benchmark Return [%] 138.837436
Max Drawdown [%] 35.49422
Max Drawdown Duration 122 days 00:00:00
Total Trades 6
Win Rate [%] 80.0
Avg Winning Trade [%] 52.235227
Avg Losing Trade [%] -3.933059
Profit Factor 45.00258
Expectancy 692.157004
Sharpe Ratio 4.078172
Calmar Ratio 23.220732
Omega Ratio 2.098986
Sortino Ratio 7.727806
Name: Close, dtype: object
Pre-requisites:
- a Binance.US API key
Environment Variables:
BINANCE
from pprint import pprint
from hyperdrive import Exchange
from Exchange import Binance
# Binance API token loaded as an environment variable (os.environ['BINANCE'])
bn = Binance()
# use 45% of your USD account balance to buy BTC
order = bn.order('BTC', 'USD', 'BUY', 0.45)
pprint(order)
Output:
{'clientOrderId': '3cfyrJOSXqq6Zl1RJdeRRC',
'cummulativeQuoteQty': 46.8315,
'executedQty': 0.000757,
'fills': [{'commission': '0.0500',
'commissionAsset': 'USD',
'price': '61864.6400',
'qty': '0.00075700',
'tradeId': 25803914}],
'orderId': 714855908,
'orderListId': -1,
'origQty': 0.000757,
'price': 0.0,
'side': 'SELL',
'status': 'FILLED',
'symbol': 'BTCUSD',
'timeInForce': 'GTC',
'transactTime': 1637030680121,
'type': 'MARKET'}
Use the scripts provided in the scripts/ directory as a reference since they are actually used in production daily.
Available data collection functions: